Using OpenAI Assistant v2 API to Build Your Own Knowledge Base Chatbot in 5 min

Some time ago, I created a blog post on how to build your own chatbot using OpenAI's Assistant API in its v1 Beta. Since then, OpenAI has introduced v2 Beta updates, and GPT-4o has been released. Let's delve into these developments to see how they can enhance our capabilities.
Assistant v2 API Updates
OpenAI has introduced some cool new features in the v2 API that we can leverage for our bots:
- Improved file retrieval & parsing - We can now import more knowledge files, parallelize them, and use them more efficiently than before. The notion of
vector storeshas been introduced, which allows for more efficient file searches. - More granularity in user control - We can adjust the temperature for bot outputs (to control creativity), change the Top P setting, which affects bot diversity, and set the maximum number of tokens to control spending.
- New models - In addition to using fine-tuned models in the v2 API, we also have the option to use OpenAI's flagship model, GPT-4o. GPT-4o is twice as fast and twice as cheap compared to GPT-4 Turbo, although it is still 10x more expensive than
GPT-3.5-turbo-0125but is worth considering if you need more power for your use case.
How to Create an Assistant?
If you followed my blog post and created a v1 bot via Playground, you should be able to easily migrate to v2 using the new API version.
If you are starting from scratch, you need to create an OpenAI account and load it with resources. Then, head over to the assistant tab and click on the Create button.
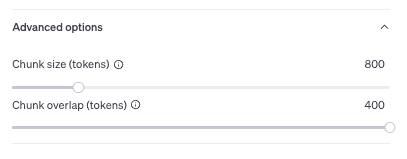
First, enter the name of your assistant. Follow the provided instructions and select a model depending on your use case and the balance between "intelligence" and the number of queries your bot will handle (knowledge size, potential user count, etc.). In the retrieval part of the menu, add files that will be your external knowledge fed into the chatbot. For this tutorial, we will go with default file storage settings.
GPT Assistant Use Case
For this example, I will be using our Bright Inventions webpage data as knowledge for our chatbot. I created the Bright assistant, a helpful bot for employees to gather more information about the company without needing to scan the entire webpage. The use cases are unlimited - for instance, you could create a chatbot for potential customers to streamline the process of verifying the company’s experience and portfolio, or a customer support chatbot to feed in company FAQ knowledge.
The site is hosted on GitHub, and the relevant knowledge is located within markdown files.
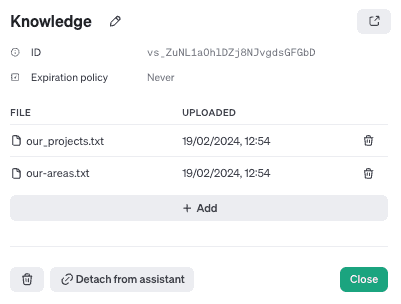
By manipulating files, I created our-areas.txt, a collection of all markdown posts from the our-areas folder, and our_projects.txt, a text file containing all merged markdown files from the projects folder. I uploaded them to my assistant and added them as knowledge.
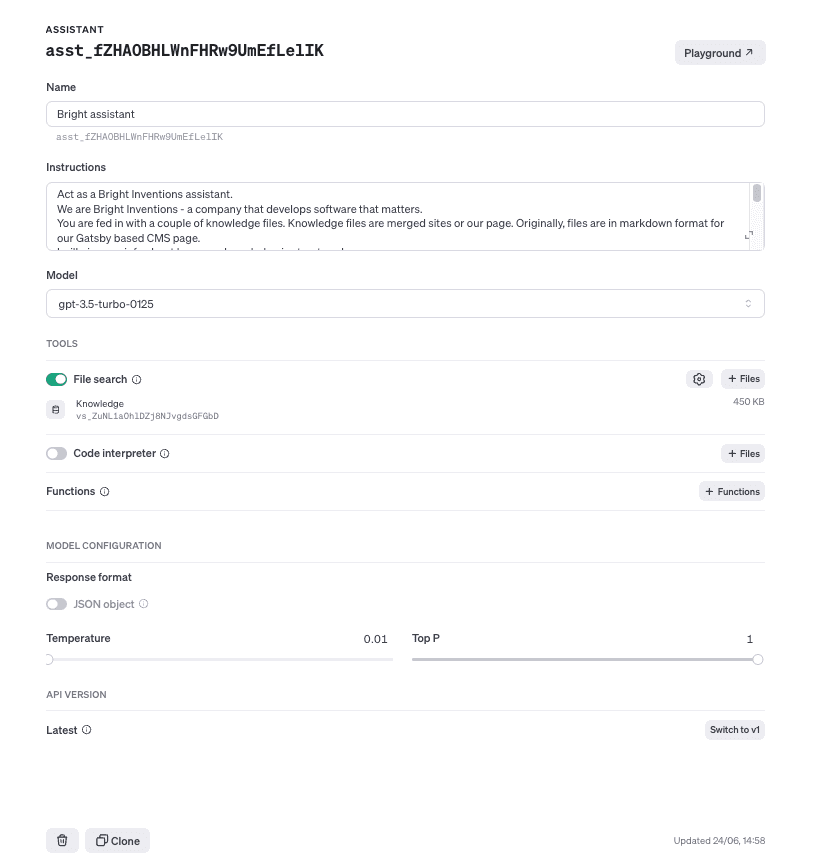
I added instructions for how the bot should behave, what knowledge was fed to it, and how the files are structured inside. I selected the gpt-3.5-turbo-0125 model for a good balance between accuracy and costs and set the temperature to the minimum to ensure the bot is not too creative.
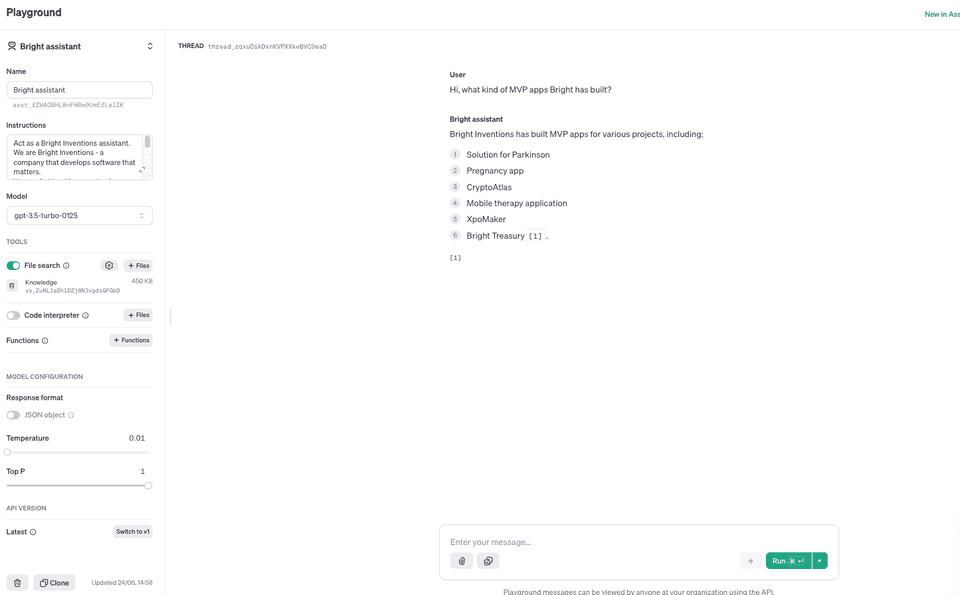
When I created my assistant, I started to test it via the playground by asking for knowledge available from the data:
Hope you enjoy the tutorial! If you created a bot with the v1 version, make sure to upgrade to v2 and check out its improved performance. You will likely save some money on queries and make the reasoning more efficient.
