POS Software Development: 2025 Guide for Custom Point of Sale System
Dive into the technical world of the POS development process. Discover key features of Point of Sale, top challenges, trends, and real case studies. Explore the guide about custom POS development based on our over a decade of experience in building, scaling, and modernizing POS systems for hospitality and retail.

Point of sale system definition
A Point-of-Sale (POS) system is a combination of hardware and software that facilitates sales transactions and manages business operations in retail, hospitality, and other industries. It includes devices like thermal printers, POS terminals, desktop and mobile POS systems, enabling businesses to process payments, track inventory, and manage orders.
POS system development can be tailored to meet specific needs such as supporting old desktop hardware which may be still used by end users, especially in hospitality. Point-of-sale software's main functionality is ensuring a smooth connection between hardware and software components. Therefore a POS developer must understand both hardware and software components to build an effective system.
Key POS features to include in modern POS software development
POS systems are versatile solutions that consist of dozens of features, additional applications, and POS hardware, forming the technological backbone for managing client orders in restaurants, hotels, and retail settings.
Examples of must-have features in POS development
- Inventory Management: Track stock levels, reduce waste, and reorder automatically.
- Integrations: Connect with POS hardware (printers, card readers) and third-party services.
- Z-Report and X-Report: Essential for daily financial summaries and cash register audits.
- Check-in/Check-out: Manage employee time tracking efficiently.
- Payment Processing: Accept various payment types.
- Order Management: Handle bundles, variants, and customizations.
- Table Management: Organize seating with a visual floor plan.
- Digital Ordering: Enable online orders.
- Payment Split: Allow customers to split payments.
- Notes for Kitchen: Special instructions for orders.
- Reporting & Analytics: Real-time data for business insights.
Extra POS Solution Features for Standout POS Application Development
- Dark Kitchen: Support for off-site kitchens.
- Splitting the Bill: Divide the bill between guests.
- Kitchen Display System: Digital kitchen orders.
- Kiosk Integration: Self-service options.
- Offline Mode: Operate without internet and sync the POS system's data as soon as the internet connection is restored.
- Cloud-Based POS: Access from anywhere.
- Delivery Management: Manage deliveries efficiently.
- Order Sync with Marketplaces: Orders from delivery platforms are available on a single POS device.
- Caller ID: Recognize regular customers during phone ordering.
POS software development: cloud POS or on-premise POS
Cloud POS and on-premise POS systems differ in their infrastructure and setup. A cloud POS operates through the internet, offering flexibility, remote access, and automatic updates. It's easier to scale but requires a reliable internet connection which can be an issue in restaurant or hotel environments.
On the other hand, traditional POS involves hosting software and hardware locally, which gives businesses more control but requires regular maintenance and higher costs.
When you build a POS system, consider business needs: cloud POS excels in flexibility and usually lower costs, while on-premise POS offers better control and offline POS capabilities. Every POS software developer must weigh the benefits and challenges of both options, including internet dependency vs. full local control.
Types of integrations with point of sale software
For POS developers and vendors, a key aspect of a POS development is its ability to reliably integrate POS with various devices and multiple third-party providers. Let’s dive into the types of POS integrations:
POS solution and hardware integrations
Check out the examples of retail devices that are part of a POS system, ranging from POS desktops, terminals, and kiosks to printers. Printers, in particular, can often present the most technical challenges.
Modern POS systems should integrate with printers wirelessly and reliably. This means that if one printer fails to print a receipt, the POS system should automatically switch to a backup printer. Be aware of common technical challenges when integrating POS systems with retail devices, especially printers.
POS and payment provider integrations
From choosing the right providers to handling the payment process, and managing daily communication with payment partners, POS providers face many challenges.
If you are at the stage of choosing a payment provider, consider answering these key questions which will help you build a well-thought-out payment solution offering a high number of payment methods.
The most popular payment global providers are Stripe, Square, and Adyen.
Read more about technical aspects of integrating payment providers with POS in our another blog post.
POS and food delivery applications integration
The most popular third-party food delivery providers include Uber Eats, Wolt, Just Eat (or local representatives like Lieferando) or Deliveroo.
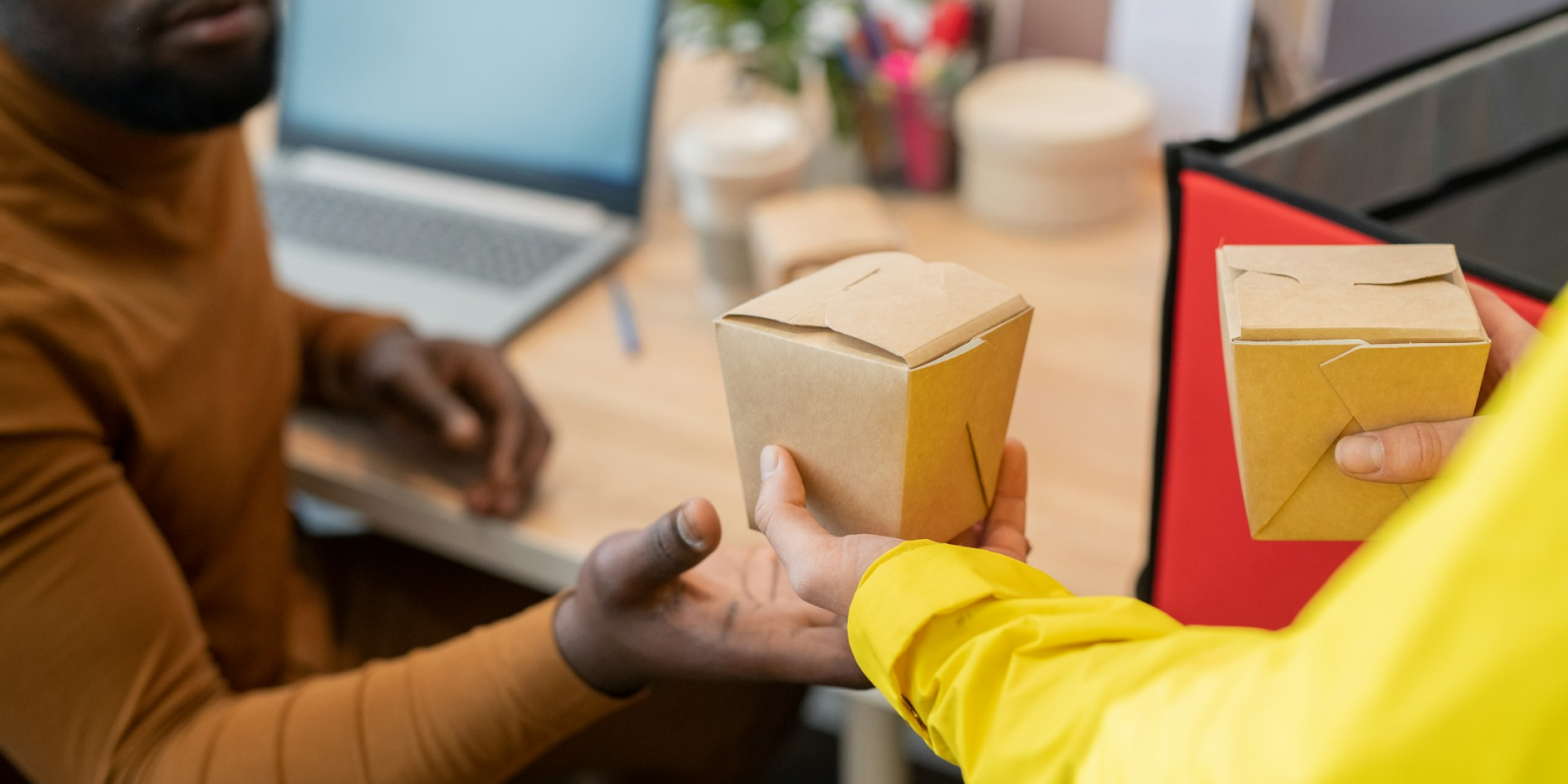

Restaurant owners are aware of the pros and cons of food delivery integrations. Technology can help minimize the drawbacks more than you might think:
Pros:
- A vital client acquisition channel.
- Support for delivery if the restaurant lacks in-house drivers.
Cons:
- High fees associated with client acquisition and delivery services.
Tech solution: A custom point of sale that offers a white-label solution enables restaurants to build their own digital ordering website, reducing the high costs associated with third-party delivery platforms.
Additionally, having a POS with an integrated delivery drivers app allows restaurant owners to manage their food delivery in-house if they choose to, offering greater control and cost savings over outsourced delivery services.
- Too many devices for staff to manage.
Tech solution: custom POS and food delivery providers integration transferring orders from external providers into one POS device.
- Restaurant menu discrepancies across platforms.
Tech solution: a proper integration with food delivery apps can sync changes from the main POS to all platforms, reducing errors and saving time.
Are you wondering whether API or FTP is the better choice for your POS and delivery software integrations? Learn more!
POS and Caller ID integration
Caller ID is a device that provides information about incoming phone numbers. With the right integration with the POS, when a staff member answers the phone, they can instantly see on-screen details if a regular customer is calling. This includes all the necessary information to efficiently process the order, such as the delivery address and phone number. This feature streamlines phone ordering and enhances the customer experience with a more personalized touch.
Check how our team took care of the POS and Caller ID integration and learn about challenges our engineers faced.

Read more about POS integration and its challenges in our another blog post.
Emerging trends in POS application development: what to expect in 2025 and beyond
Explore POS development trends.
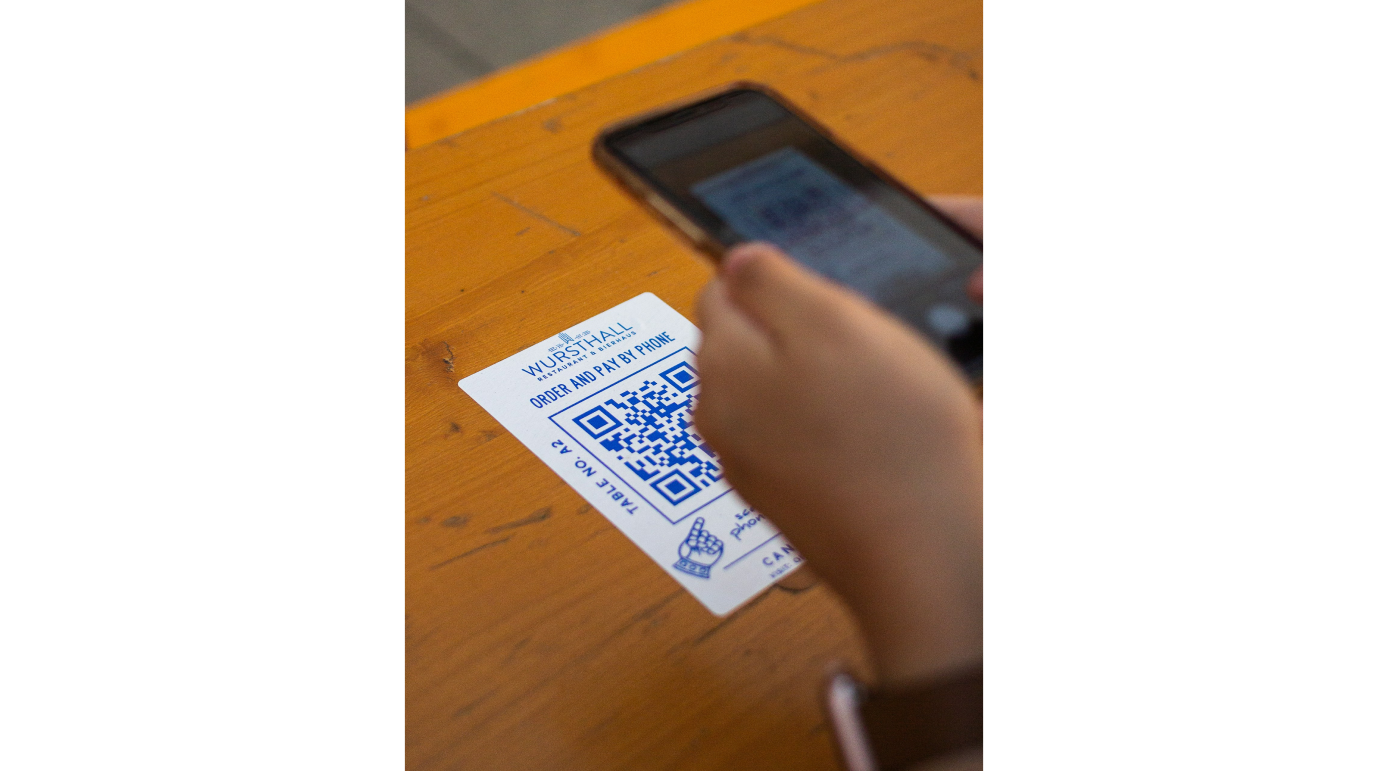
The continuous rise of QR code ordering as a response to restaurant staff shortages
QR code ordering supports busy staff by allowing customers to place orders and pay directly, which reduces wait times.
Although QR codes shouldn’t replace staff initially - clients should still be able to discuss the order with waitstaff, using QR codes for payment can alleviate pressure on staff during peak hours, improving overall efficiency and customer experience.

Transiting from paper kitchen receipts to Kitchen Display Systems (KDS)
While many establishments still rely on old-fashioned paper methods, KDS offers a more efficient, modern solution. It streamlines order management, reducing mistakes and speeding up service. Orders can be tracked and modified in real-time, improving communication between the kitchen and front-of-house staff. This shift not only cuts down on paper waste but also enhances overall workflow and accuracy in busy kitchens, optimizing food delivery time.
Check out an actual case study of Kitchen Display System and how it changed restaurant operations in the UK and Israel.
Hardware decluttering of restaurant, retail, and hotel counters
The fact that modern point-of-sale software is connected to many devices is both a benefit and a challenge in some cases. For example, taking care of multiple devices provided by different food delivery parties brings more responsibility to already busy waitstaff.
Building a custom point of sale allows all orders, whether from in-house dining, phone orders, delivery apps, or a white-label application, to be transferred into a single POS system. This means waitstaff can view and manage all orders on one device, aligning with the growing trend in POS application development aimed at eliminating the unnecessary POS devices often provided by third-party systems such as Just Eat, Uber Eats or Deliveroo.
Using AI for analytics and inventory management
With AI, restaurants can track customer preferences, predict demand, and optimize stock levels to reduce waste. AI-powered analytics allow businesses to make data-driven decisions about menu offerings, pricing, loyalty programs, and staffing, improving overall efficiency and customer experience. In inventory management, AI helps monitor stock in real-time, quickly informing about the need for ingredients reorder.
How to build a POS System that complies with local and international regulations
As a POS vendor, your POS functions have to be adjusted to local regulations and tax rules. Here are a couple of compliance issues your software engineering team has to be aware of.
Compliance with GDPR in custom POS development
During POS software development, it's critical to ensure GDPR compliance, particularly in how customer data is collected, stored, and processed. This includes securing consent for data collection, ensuring data encryption, and providing customers with the ability to request data deletion.
Compliance with PCI DSS for payment processing
To protect sensitive payment information, your POS system must comply with the PCI Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). This involves implementing data obfuscation techniques, two-fold protection of cardholder data, encryption of transmitted data, and the creation and maintenance of access logs.
Check how to get access to POS data to optimize your payment solutions at the same adhering to security regulations. Our POS application development team faced that challenge while building the bill split feature.
Adherence to local tax law during POS development
Your POS system must integrate with local tax rules, including calculating the correct sales tax and generating tax-compliant receipts. This may involve adapting the software to meet region-specific tax regulations, such as VAT or GST, and keeping up with changes in local tax laws to ensure ongoing compliance.
One example of adapting to tax rule changes is when our team implemented an amendment to the VAT law in Israel, which directly impacted invoice generation. We adjusted the restaurant invoice generation software to comply with these updates by modifying the information included in the invoices. Check out the case study to learn more about it!
The role of UX/UI in building intuitive custom POS software
From understanding the specific needs of POS system users to integrating UI/UX solutions that address their pain points, a POS software developer must follow this path during POS development.
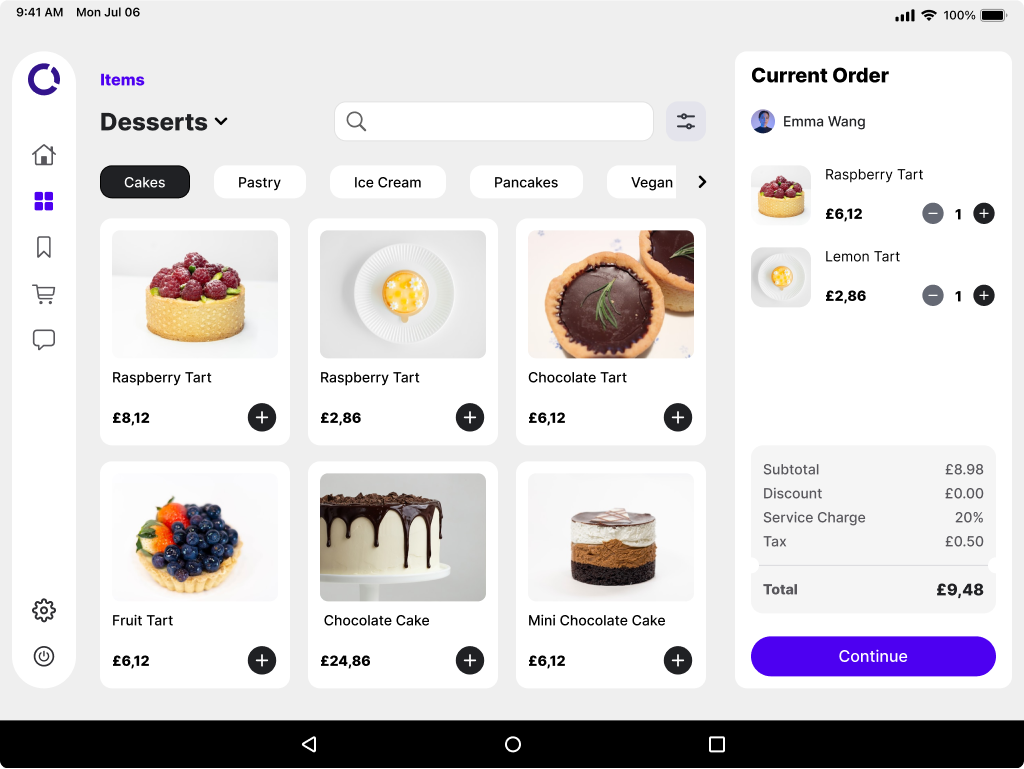
One critical feature requiring extra attention is payment processing. To ensure a smooth experience, it's essential to implement must-have UX/UI practices, such as:
- informative animations;
- iconography with labels;
- button hierarchy.
Read more about designing payment in POS and check the designs for inspiration!
The Role of User Personas in POS Application Development
User personas serve as fictional yet data-driven representations of your target users, encapsulating their behaviors, needs, and challenges. By crafting detailed personas, POS developers can tailor custom POS solutions that resonate with actual user experiences, leading to more intuitive and effective systems.
For instance, consider "Jennifer," a meticulously developed persona representing a frontline retail staff member. Her profile sheds light on daily operational challenges, such as managing customer orders and dealing with nonintuitive bill splitting. Insights from such personas guide POS developers in prioritizing features like streamlined checkout processes, real-time inventory updates, and user-friendly interfaces.
Integrating user personas into the development lifecycle ensures that the POS application aligns with real-world user expectations, enhancing usability and satisfaction.
To explore a comprehensive user persona example and understand how it can inform your POS development strategy, download the free PDF:
Free UX Resource: The POS Persona You Need

Getting feedback from point-of-sale users
Anyone developing software solutions for hospitality or retail knows that end users are busy. Even though sales assistants or waitstaff use your tools daily, they rarely have time to provide valuable feedback.
That’s why it’s the POS developer’s job to find alternative ways to gather insights without disrupting users' workflow. Discover a few tactics that can help you collect actionable feedback on your solution.
Do you want to build your own POS system?
As a POS software development company we have been creating cutting-edge POS solutions for over a decade. Contact our POS developers team to discuss cost-effective POS.

